nfc reader vs rfid reader RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. But your phone should be awake even with the passive NFC reader. On iPhone X and older models, swipe down on the right side of the notch, or swipe up from the bottom of the screen (as per your model) to open the .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid nfc reader writer
2 · nfc tag reader used for
3 · nfc rfid reader software
4 · nfc rfid reader app
5 · differences between rfid and nfc
6 · adafruit rfid reader
7 · adafruit nfc reader
02. Filter by City. 03. Filter by Genre. Listen online to the best Christmas radio stations from Alabama, United States. myTuner Radio, easy to use internet radio for free.
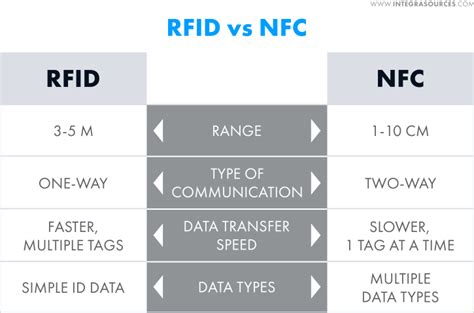
RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency . RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch . RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.
While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-physical technique used to relay information. It relies on smart tags, which are attached to objects like products in stores or animals on a farm. The smart tags work in collaboration with RFID readers, which provide power and receive the relayed identification data.In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .
However, there is a distinction between the two. Unlike RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, NFC tags have the capability to both send and receive information, allowing for two-way communication. In contrast, RFID tags are typically designed for one-way communication. RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the .
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-physical technique used to relay information. It relies on smart tags, which are attached to objects like products in stores or animals on a farm. The smart tags work in collaboration with RFID readers, which provide power and receive the relayed identification data.In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .
smart card windows 10 driver overflow
rfid vs nfc difference
smart card windows server
smart card tui
smart card troubleshooting
smart card windows 10 logon
Apple has enabled all the iPhones from iPhone 6 to the latest iPhone 12 to work with the NFC tags or cards. The NFC reader on your iPhone can read the information from an NFC tag and automate tasks for you. How .
nfc reader vs rfid reader|nfc tag reader used for