rfid system architecture Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate. Hello, A-Sven-gers! Thanks for checking out my video on using Amiibo on the Nintendo 3DS and New Nintendo 3DS handheld systems. While the New Nintendo 3DS/ N.
0 · types of rfid systems
1 · rfid schematic diagram
2 · rfid reader block diagram
3 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
4 · rfid radio frequency identification
5 · rfid full form in iot
6 · rfid full form in computer
7 · rfid block diagram
Nfc-frog. Kick-ass contactless credit card reader. With nfc-frog you can extract data from many contactless EMV credit cards. Also it supports mulitiple reading modes, so you can choose mode which suits you best. Tested with: Visa, .If you are not using Maven or some other dependency management tool that can understand Maven repositories, the list below is what you . See more
types of rfid systems
The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy .
rfid schematic diagram
Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring direct line-of .
The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.
RFID is the reading of physical tags on single products, cases, pallets or re-usable containers which emit radio signals to be picked up by reader devices. These devices and software must be supported by a sophisticated software architecture that enables the collection and distribution of location-based information in near real time. The
The basic functionality of an RFID system is asset management. The fundamental use cases are: identification, alerting, monitoring, authentication. The improved asset visibility can help prevent losses due to spoiling of perishables, theft, and counterfeiting.In Part IV, several major research challenges in the RFID field are presented, such unsatisfactory read accuracy even in the most favorable RF environments, low read ranges, security problems, localization of tags, energy harvesting and simulators and emulators for RFID systems.
This article first provides an overview of RFID systems and how they work, followed by the history of RFID, a review of recent and future RFID systems, and finally some recommendations for future work in this exciting technology.
rfid reader block diagram
The Auto-ID Lab at MIT has developed a suite of RFID and software specifications for an Electronic Product Code (EPC) network that have been incorporated into EPCglobal and ISO standards and are being used by over 1,000 companies across the globe.The basic RFID system consists of a Reader and a Transponder. The Reader or Transceiver is the unit acting as the master and supplies the RFID transponder with energy and triggers the communication signals to force the transponder to execute the requested action.This paper presents an architecture design of a networked RFID tracking and tracing system, and also proposes a data schema design for managing track and trace data. Key Words: Radio Frequency Identification, Middleware, Track and Trace, Item .Today’s RFID system architecture is carried over from the architecture used in other auto-id systems, chiefly optical barcode systems. As RFID introduces new functionalities and privacy risks, this classic architecture is no longer appropriate.
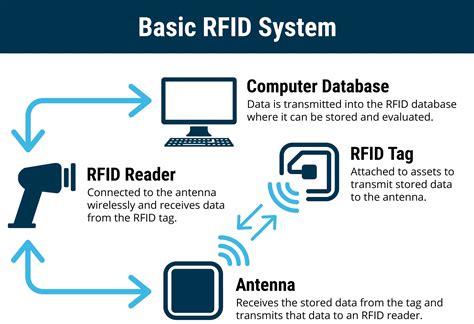
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be read from several meters away, without requiring direct line-of . The RFID systems basically consist of three elements: a tag/transponder, a reader and a middleware deployed at a host computer. The RFID tag is a data carrier part of the RFID system which is placed on the objects to be uniquely identified.RFID is the reading of physical tags on single products, cases, pallets or re-usable containers which emit radio signals to be picked up by reader devices. These devices and software must be supported by a sophisticated software architecture that enables the collection and distribution of location-based information in near real time. The
The basic functionality of an RFID system is asset management. The fundamental use cases are: identification, alerting, monitoring, authentication. The improved asset visibility can help prevent losses due to spoiling of perishables, theft, and counterfeiting.
In Part IV, several major research challenges in the RFID field are presented, such unsatisfactory read accuracy even in the most favorable RF environments, low read ranges, security problems, localization of tags, energy harvesting and simulators and emulators for RFID systems.
This article first provides an overview of RFID systems and how they work, followed by the history of RFID, a review of recent and future RFID systems, and finally some recommendations for future work in this exciting technology.The Auto-ID Lab at MIT has developed a suite of RFID and software specifications for an Electronic Product Code (EPC) network that have been incorporated into EPCglobal and ISO standards and are being used by over 1,000 companies across the globe.The basic RFID system consists of a Reader and a Transponder. The Reader or Transceiver is the unit acting as the master and supplies the RFID transponder with energy and triggers the communication signals to force the transponder to execute the requested action.
smart card emulator windows

rfid radio frequency identification tags
rfid radio frequency identification
rfid full form in iot
Reading NFC tags with the iPhone 7, 8 or X will depend on your version of operating system as follows : iOS 14 : If you have the latest iOS 14 operating system, you can read NFC tags natively with the built-in reader. Just .
rfid system architecture|rfid reader block diagram