rfid tag vs nfc tag RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information . What I am doing is that I use NFC Tools android app to save plain text and the I want to read this data in my own app> android; android-studio; nfc; reader; Share. Improve .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid tags pros and cons
2 · pros and cons of nfc
3 · nfc tags are always passive
4 · nfc disadvantages
5 · different types of rfid tags
6 · differences between rfid and nfc
7 · are nfc tags waterproof
Cloud based 13.56MHz NFC or 125KHz RFID / QR Code Reader w/ Built-in Programmable .
RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information .NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that enables the sharing of data encoded in RFID tags via RFID scanners. The term RAIN RFID specifies use of the UHF frequency band, which leverages the GS1® air interface protocol to communicate with tags.
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. Unlike RFID tags, only one tag can be read at a time with NFC technology. This can limit its use cases and means that RFID tags are often better suited to environments where there are a lot of trackable components.
While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the .
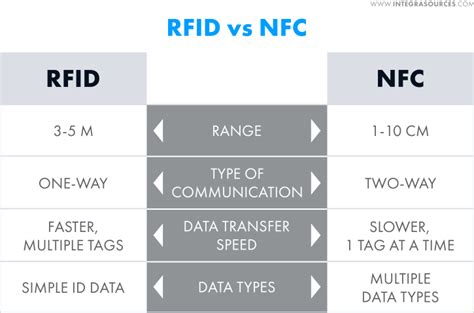
These tags are powered by the energy emitted from the RFID reader, making them cost-effective and ideal for applications where frequent tag replacement is not feasible. In contrast, NFC devices, such as smartphones, have active components that necessitate a power source, usually a built-in battery. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology. Like NFC, RFID is also a wireless communication technology that uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data between two devices. The main difference between the two technologies is that RFID is not limited to the 13.56 MHz frequency. While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that enables the sharing of data encoded in RFID tags via RFID scanners. The term RAIN RFID specifies use of the UHF frequency band, which leverages the GS1® air interface protocol to communicate with tags.
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. Unlike RFID tags, only one tag can be read at a time with NFC technology. This can limit its use cases and means that RFID tags are often better suited to environments where there are a lot of trackable components.

While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.
One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the . These tags are powered by the energy emitted from the RFID reader, making them cost-effective and ideal for applications where frequent tag replacement is not feasible. In contrast, NFC devices, such as smartphones, have active components that necessitate a power source, usually a built-in battery. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Technology. Like NFC, RFID is also a wireless communication technology that uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data between two devices. The main difference between the two technologies is that RFID is not limited to the 13.56 MHz frequency.
rfid vs nfc difference
rfid tags pros and cons

NFC stands for Near-field communication. See more
rfid tag vs nfc tag|rfid vs nfc difference