rfid tag to antenna polarization wave transmitter The wave® antenna generates five beams with multiple polarizations to uniformly illuminate an optimal zone along the length of the antenna enabling the user to read tags in any orientation. The wave antenna in it's rugged protective container. NFL top-10 rankings: Chiefs top Lions; Steelers, Bills, Eagles climb; Falcons drop out. Check out our guide to the 2024-25 NFL Playoffs including the current bracket and playoff .
0 · wave antenna rfid
1 · wave antenna
2 · rfid tags
3 · rfid tag selection guide
4 · rfid tag direction
5 · rfid antenna
6 · newave rfid antenna
7 · antenna rfid tag direction
The replacement for this product is the MIFARE Ultralight AES. NXP ® .
The wave® antenna generates five beams with multiple polarizations to uniformly illuminate an .Furthermore, the overlapping beams of the Wave® provide all 3 polarizations, whereas a patch .
The wave® antenna generates five beams with multiple polarizations to uniformly illuminate an optimal zone along the length of the antenna enabling the user to read tags in any orientation. The wave antenna in it's rugged protective container.
Furthermore, the overlapping beams of the Wave® provide all 3 polarizations, whereas a patch antenna can only provide 2 at most. This makes the Wave® ideal for item-level zone coverage of densely populated regions of RFID tagged products in warehouses, retail stores, and portals. Thus, a reader using a linearly polarized antenna will produce more reproducible read results if the antenna is vertically polarized; on the other hand, a horizontally polarized antenna will display more prominent fades but also (sporadically) read more distant tags.
Two antennas provide polarization diversity for reading an RFID tag that a single antenna is not able to read due to the tag orientation. Many of the above issues associated with conventional patch antennas are overcome by the specially designed Wave® antenna as described previously and shown below.Polarization is another important consideration for RFID reader antennas. For maximizing tag range, antenna polarization of the tag must be matched to that of the reader antenna. In most general case, both reader and tag antennas are elliptically polarized with mutually tilted axis of the polarization. The mutual polarization efficiency can be
wave antenna rfid
The polarization of a commercial antenna, particularly when encased in a plastic radome, is not so obvious, and the user must usually refer to the labeling on the antenna or the manufacturer’s data sheets, or use a linearly polarized tag to .
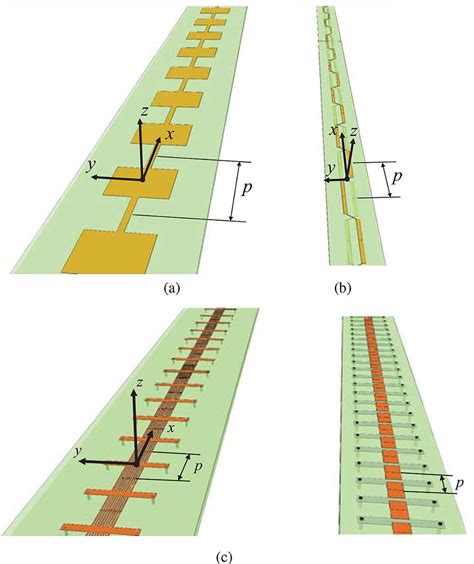
There are several different methods to describe the characteristics of a passive UHF RFID system (Braaten et al., 2006; Finkenzeller, 2003). The Friis transmission equation (Stutzman & Thiele, 1998) will be used here to show the relevant properties of an antenna on a RFID tag for achieving a maximum read range. A circular polarized RFID antenna is an antenna designed to emit and receive radio frequency signals in a circular polarization pattern. This type of antenna is commonly used in radio frequency identification (RFID) systems, where it is used to communicate with RFID tags.
Passive radio frequency identification (RFID) in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) band is attractive due to the availability of low cost tags and adequate read range for supply chain and other applications.
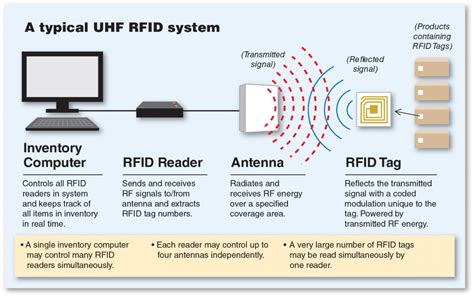
We distinguish between smaller and larger antennas, polarized omnidirectionally and directionally, left or right torsion. The RFID antenna draws power from the RFID reader. Then it sends it in the form of a radio wave to an RFID tag within its range. If the readers are the brains of the RFID system, then the antennas are its arms.
wave antenna
The wave® antenna generates five beams with multiple polarizations to uniformly illuminate an optimal zone along the length of the antenna enabling the user to read tags in any orientation. The wave antenna in it's rugged protective container.
Furthermore, the overlapping beams of the Wave® provide all 3 polarizations, whereas a patch antenna can only provide 2 at most. This makes the Wave® ideal for item-level zone coverage of densely populated regions of RFID tagged products in warehouses, retail stores, and portals. Thus, a reader using a linearly polarized antenna will produce more reproducible read results if the antenna is vertically polarized; on the other hand, a horizontally polarized antenna will display more prominent fades but also (sporadically) read more distant tags.
Two antennas provide polarization diversity for reading an RFID tag that a single antenna is not able to read due to the tag orientation. Many of the above issues associated with conventional patch antennas are overcome by the specially designed Wave® antenna as described previously and shown below.Polarization is another important consideration for RFID reader antennas. For maximizing tag range, antenna polarization of the tag must be matched to that of the reader antenna. In most general case, both reader and tag antennas are elliptically polarized with mutually tilted axis of the polarization. The mutual polarization efficiency can be
The polarization of a commercial antenna, particularly when encased in a plastic radome, is not so obvious, and the user must usually refer to the labeling on the antenna or the manufacturer’s data sheets, or use a linearly polarized tag to .There are several different methods to describe the characteristics of a passive UHF RFID system (Braaten et al., 2006; Finkenzeller, 2003). The Friis transmission equation (Stutzman & Thiele, 1998) will be used here to show the relevant properties of an antenna on a RFID tag for achieving a maximum read range.
A circular polarized RFID antenna is an antenna designed to emit and receive radio frequency signals in a circular polarization pattern. This type of antenna is commonly used in radio frequency identification (RFID) systems, where it is used to communicate with RFID tags.Passive radio frequency identification (RFID) in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) band is attractive due to the availability of low cost tags and adequate read range for supply chain and other applications.
rfid tags

advantages of smart cards for online merchants
air new zealand one smart card fees
$11.49
rfid tag to antenna polarization wave transmitter|rfid tags