rfid tag frequency RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person. $9.99
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
Power up the Nintendo NFC Reader/Writer and make sure that the system and the .
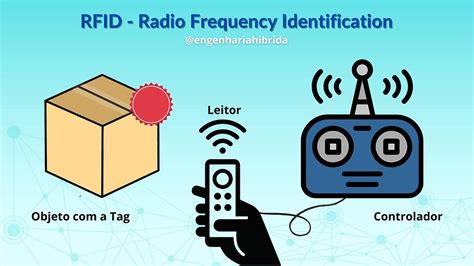
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, readers, and antennas. These components enable contactless data transmission, allowing the system to track the location, status, and information of objects.
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.Understanding Tag Size and Read Range for RFID Systems: The read range of RFID tags determines the distance at which RFID readers can detect and read them, with factors such as tag frequency, antenna design, and environmental conditions influencing this range.
What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags. RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information, which can be transmitted to an RFID reader via radio waves.The frequency that you choose will depend on the type of RFID application, whether there are any mandates to be met, such as the DoD RFID mandate, and what country the application will be used in. Low-frequency (LF) tags, for example, are better for tagging nonmetal objects that may have a high water content.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.RFID tags are categorized according to the frequency at which they are designed to operate. Four primary frequency ranges are allocated by various government authorities for use by RFID systems. • Low frequency (LF) • High frequency (HF) • Ultra high frequency (UHF) • Microwave frequency (microwave)Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, readers, and antennas. These components enable contactless data transmission, allowing the system to track the location, status, and information of objects.
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
what frequency does rfid use
ultra high frequency rfid tags
Understanding Tag Size and Read Range for RFID Systems: The read range of RFID tags determines the distance at which RFID readers can detect and read them, with factors such as tag frequency, antenna design, and environmental conditions influencing this range. What are RFID tags? Comparing ultra-high-frequency (UHF) vs. high-frequency (HF) vs. near field communication (NFC) vs. low-frequency (LF) RFID tag types. An explanation of the difference between active, passive and semi-passive RFID tags.

RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. We will review the frequencies and some of the behavioral properties of those tags in this post.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information, which can be transmitted to an RFID reader via radio waves.

rfid radio frequency identification tags

prox cards vs smart cards
When you’re done paying, a blue check mark appears on the screen. If the check mark isn’t on your screen: 1. Try to hold your phone in a . See more
rfid tag frequency|rfid radio frequency identification