rfid active tag frequency There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (un-powered) or semi-passive (battery-assisted). Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz.
The process to format an NFC chip involves writing a specific data structure to the NFC chip’s memory in a OTP (one time programable) section. Since this memory location is OTP, the .
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · rfid radio frequency identification tags
3 · rfid radio frequency identification
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · radio frequency identification tags are
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
I made this guide because none of the guides out there helped me make these cards so I figured out how to do it on my own after lots of trial and error. I ho.
The UHF frequency band spans from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, and most systems operate within the 860 MHz to 960 MHz range, depending on regional regulations. Passive UHF RFID systems can achieve read ranges of up to 12 .
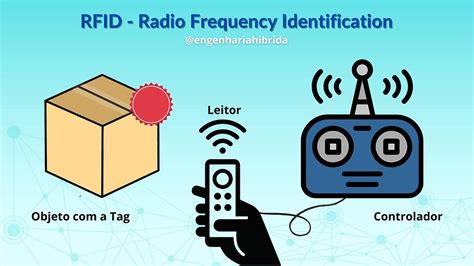
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. An RFID system consists of three main components: .The UHF frequency band spans from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, and most systems operate within the 860 MHz to 960 MHz range, depending on regional regulations. Passive UHF RFID systems can achieve read ranges of up to 12 meters and offer faster data .
The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags. The frequency range of 860–960 MHz is often referred to by a single frequency of 900 or 915 MHz.RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, readers, and antennas. These components enable contactless data transmission, allowing the system to track the location, status, and information of objects.
There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (un-powered) or semi-passive (battery-assisted). Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. Active RFID tags are radio frequency identification tags with a power source (typically a battery) with a long range — up to 150 meters (around 490 feet) or more, depending on the frequency, tag size, and antenna. (If you’re unsure what RFID is, read our introductory guide to RFID tracking.)RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. Image courtesy of EPC RFID. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags. Types of RFID Systems. Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks.
Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna.
RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency. RFID cards typically use one of these three frequencies to communicate via radio waves. Almost every RFID type we can see can be active (powered), passive (un-powered), or semi-passive (battery-assisted). The two primary types, Passive RFID and Active RFID, differ significantly in their functionalities, capabilities, and best-suited applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most suitable option for specific use cases.The UHF frequency band spans from 300 MHz to 3 GHz, and most systems operate within the 860 MHz to 960 MHz range, depending on regional regulations. Passive UHF RFID systems can achieve read ranges of up to 12 meters and offer faster data .
The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags. The frequency range of 860–960 MHz is often referred to by a single frequency of 900 or 915 MHz.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track objects. An RFID system consists of three main components: RFID tags, readers, and antennas. These components enable contactless data transmission, allowing the system to track the location, status, and information of objects. There are a variety of RFID tags on the market today, differentiated by frequency range (low, high and ultra-high). Each RFID type can be either active (powered), passive (un-powered) or semi-passive (battery-assisted). Low-frequency (LF) RFID tags: 30 KHz to 300 KHz. Active RFID tags are radio frequency identification tags with a power source (typically a battery) with a long range — up to 150 meters (around 490 feet) or more, depending on the frequency, tag size, and antenna. (If you’re unsure what RFID is, read our introductory guide to RFID tracking.)RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. Image courtesy of EPC RFID. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags. Types of RFID Systems.
Active RFID systems have three essential parts – a reader or interrogator, antenna, and a tag. Active RFID tags possess their own power source – an internal battery that enables them to have extremely long read ranges as well as large memory banks.Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna. RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency. RFID cards typically use one of these three frequencies to communicate via radio waves. Almost every RFID type we can see can be active (powered), passive (un-powered), or semi-passive (battery-assisted).
increase card rfid distance
what frequency does rfid use

Most debit and credit cards these days already have an NFC tag built-in. The aforementioned apps simply emulate these tags, with permission from the issuing bank or financial institution.
rfid active tag frequency|ultra high frequency rfid tags