how big is an rfid chip In this article, we will explore the evolution of RFID chip size, focusing on the smallest RFID chips available today. We will also discuss the applications for these tiny chips and the challenges faced in miniaturizing them. Anything will do so long as they are NFC 215 and none of the other formats. Step 1 – Setup .
0 · what is an rfid chip
1 · uhf rfid chips
2 · rfid identification chart
3 · rfid chip types
4 · rfid antenna identification
5 · rfid antenna
6 · retail rfid identification
7 · implantable rfid identification
1. Open your phone’s app store: Go to the app store on your smartphone. If you have an Android device, open the Google Play Store, and if you have an iPhone, open the App Store. 2. Search for an NFC reader app: In .
In this article, we will explore the evolution of RFID chip size, focusing on the smallest RFID chips available today. We will also discuss the applications for these tiny chips and the challenges faced in miniaturizing them.
mifare contactless card reader
LF RFID chips have a frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, they typically operate on frequencies between 125 kHz and 132 kHz. Most of the Low-frequency . In this article, we will explore the evolution of RFID chip size, focusing on the smallest RFID chips available today. We will also discuss the applications for these tiny chips and the challenges faced in miniaturizing them. LF RFID chips have a frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, they typically operate on frequencies between 125 kHz and 132 kHz. Most of the Low-frequency tags are passive tags that obtain energy from the radiation near the field of the reader coupling coil by inductive coupling.
In early 2020, MIT researchers demonstrated a terahertz frequency identification (TFID) tag that is barely 1 square millimeter in size. The devices are essentially a piece of silicon that are inexpensive, small, and function like larger RFID tags. They measure 125 micrometers (μm) by 245μm. Manufacturers were able to make smaller RFID chips using earlier technologies, but Franzon and his collaborators have not been able to identify smaller RFID chips that are compatible with the current Gen2 technology.Current smart tags usually measure 7.5 cm x 4.5 cm and are thus around the size of a credit card. For smaller goods there are also variants measuring 4.5 cm x 4.5 cm and labels for CDs and DVDs, with round paper labels to prevent imbalance with a diameter or of around 4.7 cm. 4. What are the benefits of smart tags?
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.
Standard size: These RFID chips are usually between 3 and 5 cm in size and are widely used in logistics, inventory management and asset tracking. Their larger size allows longer antennas, providing longer reading distances and better signal transmission stability.
Chip Size: The physical size of the RFID chip plays a role in determining the available memory capacity. Smaller chips might have limited memory capacity, while larger chips can accommodate more data storage.
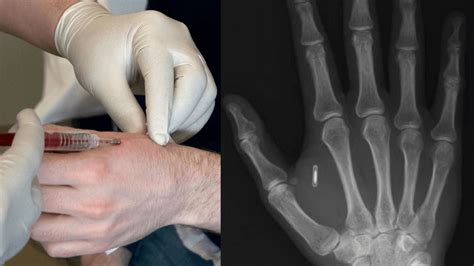
Researchers at Stanford University are currently working to create an RFID small enough to be inserted into a human cell. So far, the research team has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to 22 microns wide – one fifth the diameter of a human hair – and even embed it in the melanoma cell of a mouse.Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips. In this article, we will explore the evolution of RFID chip size, focusing on the smallest RFID chips available today. We will also discuss the applications for these tiny chips and the challenges faced in miniaturizing them.
LF RFID chips have a frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, they typically operate on frequencies between 125 kHz and 132 kHz. Most of the Low-frequency tags are passive tags that obtain energy from the radiation near the field of the reader coupling coil by inductive coupling.In early 2020, MIT researchers demonstrated a terahertz frequency identification (TFID) tag that is barely 1 square millimeter in size. The devices are essentially a piece of silicon that are inexpensive, small, and function like larger RFID tags.
They measure 125 micrometers (μm) by 245μm. Manufacturers were able to make smaller RFID chips using earlier technologies, but Franzon and his collaborators have not been able to identify smaller RFID chips that are compatible with the current Gen2 technology.Current smart tags usually measure 7.5 cm x 4.5 cm and are thus around the size of a credit card. For smaller goods there are also variants measuring 4.5 cm x 4.5 cm and labels for CDs and DVDs, with round paper labels to prevent imbalance with a diameter or of around 4.7 cm. 4. What are the benefits of smart tags? An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.Standard size: These RFID chips are usually between 3 and 5 cm in size and are widely used in logistics, inventory management and asset tracking. Their larger size allows longer antennas, providing longer reading distances and better signal transmission stability.
Chip Size: The physical size of the RFID chip plays a role in determining the available memory capacity. Smaller chips might have limited memory capacity, while larger chips can accommodate more data storage.
Researchers at Stanford University are currently working to create an RFID small enough to be inserted into a human cell. So far, the research team has been able to scale the chip and antenna down to 22 microns wide – one fifth the diameter of a human hair – and even embed it in the melanoma cell of a mouse.
what is an rfid chip
uhf rfid chips
So to read and write data to these Tags you need to transceive a byte array .
how big is an rfid chip|rfid chip types