physics and rfid chips The Physics Behind RFID. Obtain a fundamental understanding of RFID hardware. This session will cover the different frequency bands used: LF (125 KHz), HF (13.56 MHz) and UHF (860 to 960 MHz and 2.45 GHz).
If you know much about antennas, the first question you might ask is what is the operating frequency of NFC. It turns out that these devices operate around 13.56 MHz. The corresponding wavelength is 22 meters long - this means to get a .
0 · who makes the rfid chip
1 · who invented the rfid chip
2 · rfid tags for humans
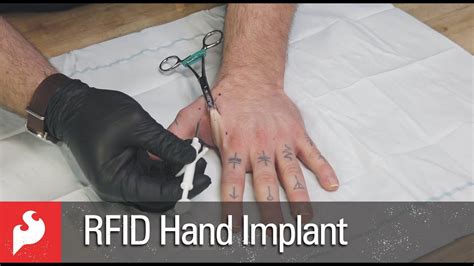
3 · rfid implants in the hand
4 · rfid chip implant near me
5 · how to disable rfid implant
6 · chip implanted in the hand
7 · chip implantation in humans
Try the Tag Reader in Control Center. If your iPhone isn’t automatically recognizing NFC tags, you can try using the NFC Tag Reader tool that’s built into your iPhone. However, this is only .
The technological advances in RFID field, in particular RFID chips, are very rapid, and today some chips have activation power as low as few μW and could integrate diverse sensing capabilities. These developments open the field of investigation for increasingly .Energy Procedia 18 ( 2012 ) 91 – 98 1876-6102 © 2012 Published by Elsevier . The energy received travels through the RFID tag's antenna and a portion of it is used to activate the chip (i.e. the Integrated Circuit, or IC) and prepare for transmission of data .
The technological advances in RFID field, in particular RFID chips, are very rapid, and today some chips have activation power as low as few μW and could integrate diverse sensing capabilities. These developments open the field of investigation for increasingly sophisticated applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) paradigm.
The energy received travels through the RFID tag's antenna and a portion of it is used to activate the chip (i.e. the Integrated Circuit, or IC) and prepare for transmission of data based on commands received from the RFID reader.The Physics Behind RFID. Obtain a fundamental understanding of RFID hardware. This session will cover the different frequency bands used: LF (125 KHz), HF (13.56 MHz) and UHF (860 to 960 MHz and 2.45 GHz). The general principle of an RFID system is based on one (or even several) readers capable of reading tags (or so-called “smart” labels), which are attached (depending on the case, glued, sewn, inserted, etc.) to an object, an animal or .
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a low-cost wireless technology that makes possible the connection of billions of things, enabling consumers and businesses to engage, identify, locate, transact, and authenticate products [1].RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Physics - understand how RFID works - how tags are able to be read and how passive RFID tags work without a battery. Similar to the conventional RFID system, there are primarily two types of harmonic RFID: (a) chipless harmonic RFID, where the ID bits are encoded in the frequency domain, and (b) chip-based harmonic RFID, where the ID bits are encoded in the time domain.Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter.
The investigations of RFID sensing techniques can be mainly divided into four categories: (1) radio frequency energy harvesting efficiency; (2) the integration of RFID and sensing techniques; (3) chip-less RFID techniques; (4) RFID sensor network technology.
who makes the rfid chip

Different RFID sensors are currently proposed in terms of architecture, complexity, and system requirements. A chip-based design, where the sensor is integrated inside the chip, provides a reliable configuration, since the sensing and communication functions are separated. The technological advances in RFID field, in particular RFID chips, are very rapid, and today some chips have activation power as low as few μW and could integrate diverse sensing capabilities. These developments open the field of investigation for increasingly sophisticated applications of the Internet of Things (IoT) paradigm.
read rfid at a distance
The energy received travels through the RFID tag's antenna and a portion of it is used to activate the chip (i.e. the Integrated Circuit, or IC) and prepare for transmission of data based on commands received from the RFID reader.The Physics Behind RFID. Obtain a fundamental understanding of RFID hardware. This session will cover the different frequency bands used: LF (125 KHz), HF (13.56 MHz) and UHF (860 to 960 MHz and 2.45 GHz). The general principle of an RFID system is based on one (or even several) readers capable of reading tags (or so-called “smart” labels), which are attached (depending on the case, glued, sewn, inserted, etc.) to an object, an animal or .
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a low-cost wireless technology that makes possible the connection of billions of things, enabling consumers and businesses to engage, identify, locate, transact, and authenticate products [1].RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Physics - understand how RFID works - how tags are able to be read and how passive RFID tags work without a battery. Similar to the conventional RFID system, there are primarily two types of harmonic RFID: (a) chipless harmonic RFID, where the ID bits are encoded in the frequency domain, and (b) chip-based harmonic RFID, where the ID bits are encoded in the time domain.
who invented the rfid chip
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. The investigations of RFID sensing techniques can be mainly divided into four categories: (1) radio frequency energy harvesting efficiency; (2) the integration of RFID and sensing techniques; (3) chip-less RFID techniques; (4) RFID sensor network technology.

rfid tags for humans

raspberry pi active rfid reader
rc522 rfid reader writer ebay
Technical Problem. Hello, I would like to access a USB ACR122U NFC reader for a project on .
physics and rfid chips|rfid tags for humans