rfid tag antenna coil Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC . Head over to the Apple Developer portal and enter your account. Find your app’s identifier (or create one) and add the NFC Tag Reading capability. Generate and download a new provisioning .
0 · rfid tag antenna types
1 · rfid scanning antenna
2 · rfid reader with antenna
3 · rfid directional antenna
4 · rfid antenna types
5 · rfid antenna size
6 · rfid antenna for sale
7 · rfid antenna design
By turning the NFC settings off or on, you can potentially resolve problems related to this feature. Step 1. Using two fingers, swipe down from the top of the screen to open the Quick settings panel. Tap More options (the .Compact, second-generation NFC card reader. Reader Lite. Supporting NFC reader and .
Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC .
In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from the tag. An RF signal can be radiated effectively if the linear dimension of the antenna is comparable with the wavelength of the operating frequency.Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC voltage is rectified to provide a voltage source for the device. As the DC voltage reaches a certain level, the device starts operating.Introduction. RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1.
The ST25 NFC (near field communication) and RFID (radio frequency identification) tags extract their power from the reader field. The tag and reader antennas are inductances mutually coupled by the magnetic field, similarly to a voltage transformer (see Figure 1).The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.This paper describes the design steps for creating and tuning an NFC/high frequency (HF) RFID antenna tuned to 13.56 MHz for the TRF79xxA series of devices. The matching network uses a 50-Ω 3-element match. A 3-element match is recommended as it allows the designer to select the required antenna quality factor (Q) for the application. Contents.RFID & NFC Transponder Coils. Great sensitivity and long read distance in transponder tags and when used as NFC/RFID antennas. Optimized for TPMS applications, high performance, harsh environments, and high temperature. View:
Coilcraft transponder coils are wirewound, surface mount antennas designed for use in a 125 kHz RFID system. They are rated for 125°C operation. Doc 397. Explore the role of transponder coils in RFID systems. With Coilcraft, learn how coil inductance affects sensitivity and read distance for optimal performance.The PA6512-AE z-axis coil is optimized for 13.56 MHz NFC/RFID tag applications and requires 85% less board space compared to antennas designed for a PCB, yet still has 50% of the read distance. Optimized for use for the Z axis in Near Field Communications systems. As illustrated in Figure 3, the reader feeds the "antenna" (really more of a coil than a conventional antenna) an oscillating signal – thanks to Maxwell's Laws that field couples to the tag's antenna (again a coil).
In a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) application, an antenna coil is needed for two main reasons: To transmit the RF carrier signal to power up the tag. To receive data signals from the tag. An RF signal can be radiated effectively if the linear dimension of the antenna is comparable with the wavelength of the operating frequency.Passive RFID tags utilize an induced antenna coil voltage for operation. This induced AC voltage is rectified to provide a voltage source for the device. As the DC voltage reaches a certain level, the device starts operating.Introduction. RFID tags extract all of their power to both operate and communicate from the reader’s magnetic field. Coupling between the tag and reader is via the mutual inductance of the two loop antennas, see Figure 1.The ST25 NFC (near field communication) and RFID (radio frequency identification) tags extract their power from the reader field. The tag and reader antennas are inductances mutually coupled by the magnetic field, similarly to a voltage transformer (see Figure 1).
The tag is composed of an antenna coil and a silicon chip that includes basic modulation circuitry and non-volatile memory. The tag is energized by a time-varying electromagnetic radio frequency (RF) wave that is transmitted by the reader. This RF signal is called a carrier signal.
This paper describes the design steps for creating and tuning an NFC/high frequency (HF) RFID antenna tuned to 13.56 MHz for the TRF79xxA series of devices. The matching network uses a 50-Ω 3-element match. A 3-element match is recommended as it allows the designer to select the required antenna quality factor (Q) for the application. Contents.RFID & NFC Transponder Coils. Great sensitivity and long read distance in transponder tags and when used as NFC/RFID antennas. Optimized for TPMS applications, high performance, harsh environments, and high temperature. View:Coilcraft transponder coils are wirewound, surface mount antennas designed for use in a 125 kHz RFID system. They are rated for 125°C operation. Doc 397. Explore the role of transponder coils in RFID systems. With Coilcraft, learn how coil inductance affects sensitivity and read distance for optimal performance.
rfid tag antenna types
The PA6512-AE z-axis coil is optimized for 13.56 MHz NFC/RFID tag applications and requires 85% less board space compared to antennas designed for a PCB, yet still has 50% of the read distance. Optimized for use for the Z axis in Near Field Communications systems.
rfid scanning antenna
can iphone read rfid

rfid chip sticker
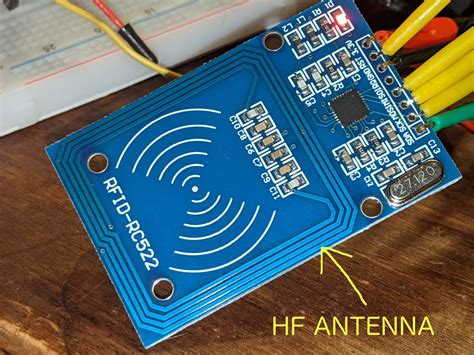
rfid reader with antenna
Raspberry PI NFC Reader Control Code. NFC readers are used for reading data from RFID cards. These cards are radio frequency ID cards which can send data without battery. Electricity is generated in the cards from the electromagnetic .
rfid tag antenna coil|rfid antenna design